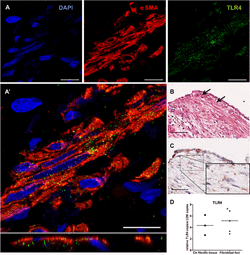
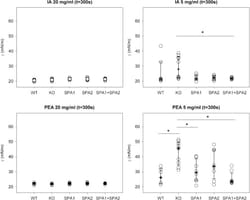
Lopez-Rodriguez, E., Gay-Jordi, G., Mucci, A., Lachmann, N., Serrano-Mollar, A.: Cell Tissue Res. 2017;367(3):721-35.
To have more information about this article, contact us:

Lung surfactant is a complex mixture of lipids and proteins lining the alveolar epithelium. At the air–liquid interface, surfactant lowers surface tension, avoiding alveolar collapse and reducing the work of breathing. The essential role of lung surfactant in breathing and therefore in life, is highlighted by surfactant deficiency in premature neonates, which causes neonatal respiratory distress syndrome and results in early death after birth. In addition, defects in surfactant metabolism alter lung homeostasis and lead to disease. Special attention should be paid to two important key cells responsible for surfactant metabolism: alveolar epithelial type II cells (AE2C) and alveolar macrophages (AM). On the one hand, surfactant deficiency coming from abnormal AE2C function results in high surface tension, promoting alveolar collapse and mechanical stress in the epithelium. This epithelial injury contributes to tissue remodeling and lung fibrosis. On the other hand, impaired surfactant catabolism by AM leads to accumulation of surfactant in air spaces and the associated altered lung function in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP). We review here two recent cell therapies that aim to recover the activity of AE2C or AM, respectively, therefore targeting the restoring of surfactant metabolism and lung homeostasis. Applied therapies successfully show either transplantation of healthy AE2C in fibrotic lungs, to replace injured AE2C cells and surfactant, or transplantation of bone marrow-derived macrophages to counteract accumulation of surfactant lipid and proteinaceous material in the alveolar spaces leading to PAP. These therapies introduce an alternative treatment with great potential for patients suffering from lung diseases.